Getting the proper brain tumor treatments is highly important. However, the correct treatment to use depends on a few factors:
The type of tumor diagnosed its size, its location within the brain and its overall prognosis. Other factors considered are its grade, the patient's general health status, and other disorders, etc.
Brain tumors are classified into two main types: benign and malignant.
A benign tumor usually grows at a slow pace and does not cause many symptoms. In such cases, the patient’s medical condition will be kept under close check by frequent monitoring and scans.
This treatment form is also known as active monitoring. In cases belonging to the category of malignant brain tumors, which are fast-growing and life-threatening, the patient will be required to undergo surgical procedures. These procedures include neurosurgery, radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy.
These treatment options are used either alone or in combination with other treatment modalities to control the growth of cancerous tumors.
Let's have a look at the various brain tumor treatments
Brain Surgery (more info) – This operative method of treatment is used for the following reasons:-
(i) To perform a biopsy for a definitive diagnosis
(ii) To remove the tumor
(iii) To de-bulk most of the brain tumor (also known as subtotal resection) in order to slow growth
(iv) To remove either the whole or a portion of a benign tumor which is recurring or growing
(v) Surgery enables the specialists to insert chemotherapy tabs or wafers in the tumor mass (vi) Drain the fluid within the tumor by inserting a tube
(vii) To place a small capsule under the scalp and allow chemotherapeutic agents to be injected for better results.
Thus, surgery is sometimes recommended to remove the entire mass of abnormal tumor cells but is also used to halt its growth. In some cases where total removal is not safe, it is still advisable to undergo surgery and prevent the tumor from encroaching on other vital structures.

Types of Surgery Performed On the Brain
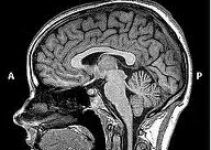
A biopsy (as shown in the above image) is required to know exactly which type of tumor is in the patient’s brain. Once the anesthesia takes effect, the neurosurgeon will drill a burr hole in the skull to facilitate the entry of an ultra-fine needle. This thin needle enters the tumor to extract a small section that is sent for a thorough microscopic examination. The details and staging help the team of doctors to decide and finalize an effective treatment plan for the patient.
Guided Biopsy
For tumors seated deep in the brain structure or those that are widespread, a guided biopsy is suggested. A CT Scan or MRI Scan enables the surgeon to maneuver the biopsy needle in the correct direction for sample extraction. This procedure utilizes sophisticated imaging techniques, hence is completely safe. Once the specialists know about the brain tumor they are dealing with, the next operation can be planned.
Craniotomy– The most commonly performed operation for brain tumors is Craniotomy.

Under general anesthesia, the specific location where the tumor is located is sliced open. It’s quite possible that the patient might even be kept conscious during the procedure and only the area of the operation is numbed. The patient's response helps surgeons to assess the brain’s functionality and response, especially in those areas of the brain that deal with functions of speech and movement. In high-grade tumors, maximum resection is carried out.
During the operation, if needed, a neurosurgeon places some tabs into the affected region. The purpose is to release chemotherapeutic agents to destroy the remaining abnormal cells.
Microsurgery- This surgery is carried out via a powered microscope. This helps the neurosurgeons to easily differentiate between healthy and unhealthy tissue. Thus, thorough removal is achieved through this operation.

Ultrasonic Aspiration – This is another mode of surgical intervention that involves breaking and removing brain tumors. A small ultrasonic probe is introduced in the tumor mass which produces sound waves. These vibrations disintegrate the tumor, which is then retrieved by gentle suction.
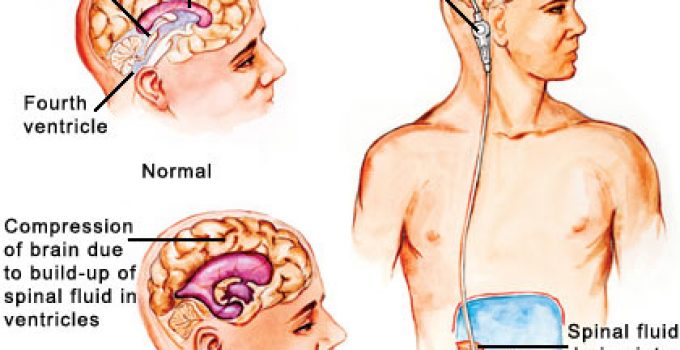
Shunts– Certain brain tumors impede or completely block normal cerebrospinal fluid circulation around the brain and spinal cord.
This leads to a buildup of the fluid within the skull. Such a condition is known as hydrocephalus. It is thus important for the doctors to drain out all excess fluid as soon as possible to relieve the elevated pressure in the head. They make use of ventriculoperitoneal shunts for this purpose. Due to the valves present in such shunts, the fluid drains away and does not re-enter.

Radiotherapy- A radiation beam consisting of high energy gamma or x-rays is targeted at the tumor cells and tissue to destroy them without causing much damage to the unaffected brain tissue. The beam results in the inability of the tumor cells to divide and reproduce. This therapy is used either as an alternative to neurosurgery or in conjunction with surgery. This painless mode of treatment is administered daily for two to six weeks.
Another variant of radiotherapy is gamma knife radio-surgery. It is a single treatment mostly used for meningiomas or neuromas. Entire brain radiotherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy are also delivered from outside.
Chemotherapy- Certain potent medicines are used for the destruction of cancer cells in the form of injections, oral tablets, surgically placed wafers or intravenous administration. Their mechanism of action is to interrupt the cell division of tumor cells. The few chemotherapy medications that render effective results in cases of brain tumors include Temozolomide, Lomustine (CCNU) and carmustine. As some normal cells get affected by this treatment, it is administered in cycles, giving time for the healthy cells to regenerate. This helps particularly in those brain tumors that re-grow even after treatment.
Medications- Certain medicines are also used for control of symptoms that surface either pre or post the surgery. Steroids are prescribed by doctors to minimize the swelling of the tumor. Anti-convulsants are recommended to fight seizure attacks.